Technology News
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. (Wikipedia)
The spectrum is broadly categorized into two types of electromagnetic radiation: ionizing and non-ionizing.
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation has a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than non-ionizing radiation and can be a serious health hazard. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing, Exposure to ionizing radiation can cause burns, radiation sickness, cancer, and genetic damage. The region at which radiation becomes considered as "ionizing" is not well defined, since different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. Higher frequency ultraviolet radiation from the sun causes molecular damage (i.e. sunburn).
Non-ionizing Radiation
Despite the upper frequencies of non-ionizing radiation (much of the spectrum of ultraviolet light and some visible light) being capable of non-thermal biological damage similar to ionizing radiation, non-ionizing radiation is being publicized as safe because it generally passes the thermal test. In 2011, the International Agency for Research on Cancer stated that there could be some risk from non-ionizing radiation to humans based on an increased risk for glioma, a malignant type of brain cancer, associated with wireless phone use (press release). More than 10,000 peer-reviewed scientific studies demonstrate harm to human health from radio frequency (RF) radiation. (link) (link) (link)
Thermal Test
A thermal test is an applied measure of temperature after exposure to radiation for 6 minutes. If the exposed area does not heat, then the frequency is safe. However, the thermal test was established in 19xx and is considered out-of-date by many of today’s scientists. [citation needed]
For reference purposes, the spectrum is defined by uses and bands. “Radar” was the first use of microwaves.
Today the use of the radio spectrum is strictly regulated by governments, coordinated by a body called the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) which allocates frequencies to different users for different uses. Another key standards organization is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). There are also EU/NATO/USECM designations. Over the years, several often-conflicting band designations have been established based on different uses. (Wikipedia)
See also:
EMF and electric vehicles (10-Sep-2022)
Charting the Electromagnetic Spectrum
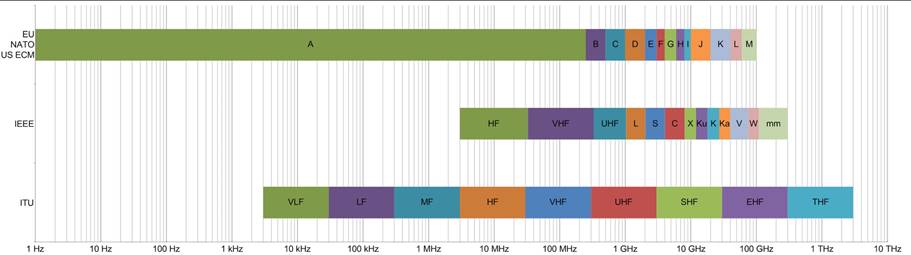
Figure 1 By Treinkvist - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=42989905
From a consumer’s perspective, general use is shown in the following diagram:
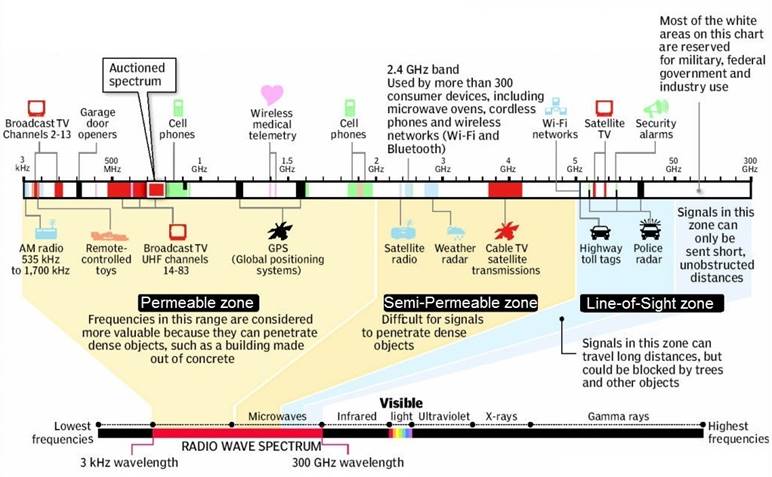
General Spectrum Details
|
Category |
Band Name |
Hertz |
Giga Hertz |
Use |
Comments |
|
Schumann Resonance 7.83 Hz |
Schumann Resonance |
7.83 Hz |
|
- Earth’s frequency - Alpha brain wave state of relaxation |
|
|
Audible Range 20 Hz – 20 kHz |
Audible Range |
20 Hz – 20kHz 2 kHz - 5 kHz sensitive |
|
|
- Measured in pitch (Hz) and loudness (dB) - article |
|
|
Power Lines |
50 Hz – 60 Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 kHz to 150 kHz |
|
RFID (LF) 125 kHz or 134 kHz (max 10 cm distance) |
Dirty Electricity Explained (8 mins)
At frequencies above 2 kHz the energy flows internal to the human body and is much more harmful (youtube 1:25)
LF low frequency |
|
|
Cellular (5G) low band frequency upper limit |
1 GHz |
|
|
Low band refers to frequencies below 1 GHz. In the low-band 5G is able to achieve speeds between 30 Mbit/s and 250 Mbit/s. (website) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Radio Frequency (RF) 20 kHz to 300 GHz |
Radio Wave Spectrum |
20 kHz to 300 GHz
|
1,000 Hz = kHz (kilo) 1,000 kHz = MHz (mega) 1,000 MHz = GHz (giga) 1,000 GHz = THz (tera) |
|
|
|
|
Permeable Zone – frequencies can penetrate dense objects (i.e. buildings) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AM |
535 kHz to 1.7MHz |
|
AM Radio |
|
|
|
Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) |
3 to 30 Hz |
|
|
Wavelength = 100,000 to 10,000 kms respectively |
|
|
|
|
|
Broadcast TV Channels 2-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remote controlled toys |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Garage Door openers |
|
|
|
Dirty Electricity in AC starts |
2,000 Hz or 2 kHz |
|
|
|
|
|
Radar: High Frequency (HF) |
3 MHz to 30MHz |
0.003 to 0.03 GHz |
RFID (HF) 13.56 MHz (up to 1 m distance) |
Wavelength = 100 to 10 metres respectively HF High frequency |
|
|
Radar: Very High Frequency (VHF) |
100 MHz |
0.03 to 0.3 GHz |
|
|
|
|
Radar: Ultra High Frequency (UHF) |
300 MHz |
0.3 to 1 GHz |
|
Wavelength = 1 metre |
|
|
New Radio (NR) / sub-6GHz |
450 MHz |
|
|
Frequency Range 1 start. Bands #1-255. NR overlaps 4G LTE. |
|
|
|
500 MHz |
|
Broadcast TV UHF channels 14-83 |
|
|
|
Lowband |
600 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
700 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
868 MHz |
|
RFID (UHF) 860-960 MHz (10-15 m distance) (source) |
UHF Ultra high frequency |
|
|
|
900 MHz |
|
Common cell phone |
|
|
|
Cellular (5G) mid band frequency range |
1 GHz to 6 GHz |
|
|
Mid band refers to frequencies in the range of 1 GHz to 6 GHz. In the mid-band 5G is able to achieve speeds between 100 Mbit/s to 900 Mbit/s. (website) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Radar: Long Wave (L) |
1-2 GHz |
1 to 2 GHz |
1090 MHz Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) used by airplanes (limited to 250-450km / 150-25 miles) |
|
|
|
|
~1.25GHz to ~1.6 GHz |
|
Global Positioning Systems (GPS) |
|
|
|
|
1,900 MHz (1.9GHz) |
|
Common cell phone |
|
|
|
Radar: Short Wave (S) |
2-4 GHz |
2 to 4 GHz |
|
|
|
|
Microwaves Permeable zone – top end / Semi-permeable Zone (difficult for signals to penetrate dense objects) |
2 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~2.25 GHz |
|
Satellite Radio |
|
|
|
|
2.4 GHz |
|
300+ consumer devices including microwave oven microwaves phones, wireless networks (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) |
|
|
|
|
2.45 GHz |
|
Microwave ovens |
|
|
|
|
~2.9 GHz |
|
Weather Radar |
|
|
|
|
3.5 GHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
~3.8GHz to ~4.1 GHz |
|
Cable TV Satellite |
|
|
|
Semi-permeable zone – top end / Line of Sight Zone (long distance) |
~4.9GHz |
|
|
Signals here can travel long distances but easily blocked by trees, etc. |
|
|
|
5 GHz, 5.6 GHz |
|
Wi-Fi, WiMax, highway toll tags |
|
|
|
4G/New Radio (NR) top end |
6 GHz |
|
|
Frequency Range 1 end |
|
|
|
|
|
Satellite TV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Security Alarms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Police Radar |
|
|
|
Millimeter Waves – 5G (mmWave) |
24,250 MHz (~24GHz) |
24 GHz aka “millimeter” |
|
Frequency Range 2 start. Bands #257-511. |
|
|
Cellular (5G) high band frequency range |
24 GHz to 40 GHz |
|
In Canada all major carriers have implemented 5G in the low and mid frequency bands. There is currently no timeline for mmWave 5G in Canada. See this post for more on the mmWave topic. |
High band refers to frequencies in the range of 24 GHz to 40 GHz. In this band, 5G is able to achieve gigabit per second speeds. (website) |
|
|
|
26GHz |
|
Optimal signal multiplication resonance frequency of graphene |
|
|
|
Extremely High Frequency (EHF) |
30GHz – 300 GHz |
30 GHz – 300 GHz “millimeter” |
|
|
|
|
Line of Sight Zone (short distance) |
50 GHz |
|
|
Signals above here can only be sent short, unobstructed distances. |
|
|
|
52,600 MHz (~52GHz) |
|
|
Frequency Range 2 end |
|
|
|
95 GHz |
|
Active Denial System (ADS) weapon system |
3.2 mm wavelength |
|
|
5G top end |
300 GHz |
110 to 300 GHz “millimeter” (IEEE) |
|
Wavelength = 1 millimetre |
|
Infrared Wave Spectrum 300 GHz – 430 THz |
Infrared Wave Spectrum |
300 GHz – 430 THz |
1,000 GHz = 1 terahertz (THz) |
|
Millimeter band = “sub terahertz”? |
|
Visible Light 430 THz – 750 THz |
Visible Light |
430 THz – 750 THz |
|
|
|
|
Ultraviolet (ionizing) |
Ultraviolet |
|
|
Ionizing |
|
|
X-rays (ionizing) |
X-rays |
|
|
Ionizing |
|
|
Gamma-rays (ionizing) |
Gamma-rays |
|
|
Ionizing |
|
[Check this: PCS & AWS bands? Used to backhaul its wireless traffic? (article)]
“back-hauling” – in a telecommunications network, the backhaul port of the network is the links between the backbone and the sub networks. A backhaul connection is defined by who operates and manages the link and who takes responsibility for connection/uptime. (Wikipedia) Backhaul basically refers to the the hosting carrier.
Sources:
Common cell phone frequencies 900 Mhz, 1900 MHz (article)
Personal radio frequency meter: RTV, wireless, lan & GPS channels, wireless telephones, test benches, leaks from microwave ovens
Safety limit: 3-6 microwatts per square metre
2007 proposal increased the safety limits to 100-1000 microwatts per square metre (not dangerous but not great for the human body)
“5G in lowband spectrum like 600MHz doesn't perform much better than high-end LTE networks.” (article)
PCS & AWS bands? Used to backhaul its wireless traffic? (article)
Sprint owns vast stretches of midband spectrum (article)
Verizon is using highband spectrum (article) (supports super-fast 5G connections but can only travel a few thousand feet)
T-Mobile is using lowband spectrum (article) (600MHz) (can push signals across miles but can't carry as much data). T-Mobile owns around 31MHz of lowband spectrum in the USA and plans to devote 10MHz to 5G downloads. T-Mobile in Hawaii owns 40MHz of lowband spectrum and may dedicate 15MHz to downloads & uploads.
According to Mediatek in March 2018:
The initial roll-out of 5G cellular infrastructure will focus on enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to provide increased data-bandwidth and connection reliability via two new radio frequency ranges:
Frequency Range 1 overlaps and extends 4G LTE frequencies, operating from 450 MHz to 6,000 MHz. Bands are numbered from 1 to 255 and this is commonly referred to as New Radio (NR) or sub-6GHz.
Frequency Range 2 operates at a much higher 24,250 MHz (~24GHz) to 52,600 MHz (~52GHz). Bands are numbered from 257 to 511 and this is commonly referred to as millimeter wave (mmWave), even though strictly speaking the ‘millimeter’ frequency length starts at 30 GHz [s/b 300 GHz?].
Return to AWARE-Ontario.ca Home Page
List of Ontario’s Issues
Disclaimer: This information has been compiled through private amateur research for the purpose of allowing the reader to make an informed and educated decision. However, while the information is believed to be reliable, accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed.
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A
https://awareontario.nfshost.com/AWARE-Ontario/Issues/Tech_Wireless/EMF_Spectrum.htm
APPENDIX B - 5G Comment
https://www.5gspaceappeal.org/the-appeal --> see footnotes [10] & [11] for information referring to more than 10,000 peer-reviewed scientific studies demonstrating harm to human health from RF radiation as well as [12] thru [27] for EMF effects.
APPENDIX C – Real Time Tracking
Vaccinated People Are Being TRACKED in Real Time via 5G Cellular [?]
CPU at 496.580 MHz
As a computer tech this looks feasible. I have questions such as why the query language and its responses are in English? (If the database was setup by westerners it would make sense, however, the Elbrus 2000 (e2k) and MCST chip are Russian.) How did the narrator know/change the password associated with his friend? Is the CPU frequency different for each person? How are individuals identified? Is 5G already rolled out to the Russia’s residences (since the guy was sleeping) when it is not rolled out here yet?
Interesting …
APPENDIX D – Music Frequencies
Dr. Leonard G. Horowitz
Musical Cult Control – the Rockefeller Foundation’s war on consciousness through the imposition of A=440Hz standard tuning (demonic?)
- Medical Veritas
Circular Music Matrix
9 core creative frequencies to the universe = Perfect Circle of Sound
396, 417, 528, 639, 741, 852, 963,
741 = Devil’s Tone, jarring harmony, causes dissonance, augmented 4th/diminished 5th
D major has F sharp (devil’s tone) at heart (huge implication on spirituality)
APPENDIX E – TETRA
TETRA, or Terrestrial Trunked Radio is a global Land Mobile Radio (LMR) open standard for digital trunked radio technology. The standard was developed by public safety and two-way radio industry experts together with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to ensure TETRA portable / handheld, mobile / vehicle-mounted and fixed-base devices, as well as the network infrastructure, provide secure, reliable and instant voice and data communications in mission critical, operations critical and business critical environments.
