Technology News
5G Technical Specifications
What is 5G?
Here is an introductory video: How exactly does 5G work? (15 mins)
Here is an introductory page: What’s the Problem with 5G? (.pdf)
3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3gpp.org) is a global umbrella for a number of standards organizations which develop protocols for mobile telecommunications. The project headquarters is located in France. (Wikipedia)
3GPP overview of specific technical requirements laid out as the 2020 minimum requirements in Release 15 (article):
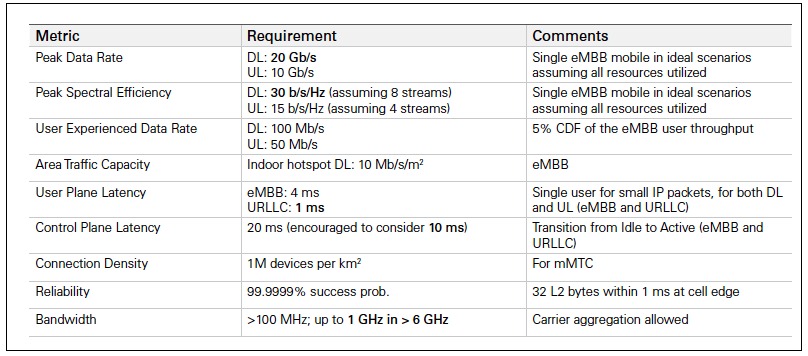
The specifications for 5G are currently being defined and is complicated. Components involved are:
- Frequency (pace)
- Amplitude (power)
- Emission i.e. 100 MHz of spectrum in the C-band at 3.5 GHz
- Pulse (beats)
- Specific energy absorption rate (SAR)
- Intensity (power density - volts per metre)
- Polarity
- Information content
- Backhauling (mesh network)
- Dielectric lens / phased array
“With 5G, data is transmitted at higher quantities and speeds, which causes the processor to consume more energy,” a Samsung spokeswoman told the Wall Street Journal. (article)
Generally, 4G networks use frequencies below 6 GHz while 5G uses extremely high frequencies in the 30 GHz to 300 GHz range. (article)
Link to "Everything you need to know about 4G LTE in Canada" article by Daniel Bader.
5G NR (New Radio)
5G NR (New Radio) is a new radio access technology (RAT) developed by 3GPP for the 5G (fifth generation) mobile network. It was designed to be the global standard for the air interface of 5G networks.
5G NR uses two frequency ranges:
Frequency Range 1 (FR1), including sub-6 GHz frequency bands
Frequency Range 2 (FR2), including frequency bands in the mmWave range (24–100GHz)
Europe
- 5G will make use of 3 frequency ranges: (link)
1. low-frequency 700MHz “coverage layer”
2. 3.4-3.8GHz band which will be the primary bandwidth
3. “super data layer” in the higher frequency 24.25-27.5GHz band
4. In March 2018, European Union lawmakers agreed to open up the 3.6 GHz and 26 GHz bands by 2020 (link)
North America
Wikipedia (link)
The frequency spectrum of 5G is divided into low-band, mid-band, and millimeter waves.
Low-band uses a similar frequency range as 4G (below 6 GHz).
5G mid-band is the most widely deployed, in over 30 networks. Frequencies deployed are from 2.4 GHz to 4.2 GHz. Sprint and China Mobile are using 2.5 GHz, while others are mostly between 3.3 and 4.2 GHz. Speeds in a 100 MHz wide band are usually 100–400 Mbit/s down. In the lab and occasionally in the field, speeds can go over a gigabit per second.
5G millimeter wave is the fastest with actual speeds often being 1–2 Gbit/s down. Frequencies are above 24 GHz, reaching up to 72 GHz, which is above the extremely high frequency band's lower boundary.
USA
- Auctioned off first bandwidth for 5G: 28 GHz (link)
Canada
Kelowna, B.C. – announced Canada’s first 5G smart city pilot project with Rogers and the University of British Columbia in May 2020
Variations by Country
Different countries are reserving different spectrum allocations for 5G. Different companies are buying/leasing different ranges of spectrum (so asset varies country to country.)
Not all of the large frequency range above will be used as available frequency zones differ between countries, so different sub-slices will be available depending on where the device operates. This has posed a huge technical challenge for smartphone design (or specifically, 5G modem designers), that have to minimize design costs with a single, simple platform, while also supporting all the possible combinations of frequencies with best performance, connection reliability and power efficiency. (article)
5G Roll-out map: Ookla 5G Map / @Ookla5GMap
Bermuda – opens inquiry into 5G (24-Aug-2020)
Timeline (chronological order)
|
Date |
Event |
|
2018-12 |
AT&T invitational 5G system available in parts of 12 cities.
|
|
2019-04 |
5G patents are dominated by Chinese companies (article) Coronavirus setting back 5G phone service expansion plans (article)
|
|
2019-04-03 Official Launch World First |
South Korea – launched on April 3, 2019 at 11pm by gov’t with SK Telecom, KT, LG Uplus (article) (article). Plans for 85 SK cities by end of 2019. [3.5GHz non-standalone (NSA) network (article)] |
|
2019-04-03ish |
Samsung & LG launched 5G smartphones. |
|
2019-04-04 |
USA Chicago and Minneapolis – hours after South Korea by Verizon (article); plan for 30 US locations by end of 2019. |
|
2019-04-26 |
3GPP release 15 – the first full set of 5G standards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2019-10 / 2019-11 |
5G phone demand decreases in South Korea due to consumer complaints over quality of networks (article) |
|
2019-12-6 |
T-Mobile launches lowband 5G (article) |
|
|
|
|
2020-02 |
Samsung launches Galaxy S20 series |
|
2020-03 |
Samsung launches unlocked S20 in North America. More affordable 5G phones to be launched in Korea in first half of 2020. |
|
2020-03 |
March 2020 Xiaomi Corp unveils 5G smartphone
|
|
2020-04 |
April 2020 Spain, Italy, France, Austria postponed auctions for 5G spectrum due to coronavirus(article)
|
|
2020-04-01 |
South Korea marks over 5 million 5G subscribers (article) |
|
2020-04-20 |
GCI begins rolling out 5G in Alaska with Ericsson (article) 600MHz spectrum. Starting in Anchorage, Wasilla, Juno, Fairbanks. Upgrading 80 towers from 15MHz to roughly 60MHz. The company is deploying LTE into its PCS, AWS, 700MHz and 850MHz bands, and 5G into its 600MHz spectrum. It's also adding LTE technologies including 256 QAM, three-channel carrier aggregation and 4x4 MIMO. |
|
|
Japan plans full 5G by 2020 Tokyo Olympics. (article)
|
|
2020-05 |
City of Kelowna announces Canada’s first 5G smart city pilot project with Rogers and the University of British Columbia (link) See AO News – Tech BC |
|
2020-06 |
3GPP release 16 expected (article) |
|
2020-07-16 |
China launches 6G satellite (article) |
|
2020-fall |
Apple to launch 5G iPhone. |
|
|
|
News 5G+ Technical Specifications (reverse chronological order)
|
Date |
Source |
Title |
Comment |
|
2021-07-08 |
Bitchute / FalconsCAFE |
A Technical Perspective With Mark Steele (50 mins)
|
Mark Steele |
|
2020-07-16 |
Independent.co.uk |
6G will bring “Digital Twins”, Samsung Says – and it’s Two Years Ahead of Schedule
|
Anthony Cuthbertson |
|
2020-07-02 |
Youtube / Safe Electrowaves |
5G & 60 GHz – Beam me up, Scotty! (20 mins)
|
Flemming Blicher, Telecom Engineer & MBA |
|
2020-03-17 |
Lightreading.com |
Study: Huawei was the biggest contributor to 5G standards
|
Mike Dano |
|
2019-04-05 |
Lightreading.com |
Another set of 5G standards was just released, but no one really cares
|
Mike Dano |
|
2016-08-08 |
US National Library of Medicine National institutes of Health |
Shin Koyama, Eijiro Narita, Yoko Shimizu, Yukihisa Suzuki, Takeo Shiina, Masao Taki, Naoki Shinohara, and Junji Miyakoshi |
More Information
International Appeal “Stop 5G on Earth and in Space”
Physicians for Safe Technology
Techblog.comsoc.org (IEEE Communications Society)
Podcasts by Matt Cossey certified electromagnetic radiation specialist in Sydney, Australia. “I am out there in the field testing this stuff with the most advanced equipment available.”
(biome-living.com)
David Ike’s linking 5G to corona virus video
Official EME reports from telecom cos – some of these cell towers radiation levels increasing up to 15 times more radiation exposure
Professor Olle Johansson
Dr. Devra Davis (HUJI) (60 mins)
Appeal to the Government of Canada (www.appel5gappeal.ca)
International Appeal “Stop 5G on Earth and in Space”
Return to AWARE-Ontario.ca Home Page
List of Ontario’s Issues
Disclaimer: This information has been compiled through private amateur research for the purpose of allowing the reader to make an informed and educated decision. However, while the information is believed to be reliable, accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A
https://awareontario.nfshost.com/AWARE-Ontario/Issues/Tech_Wireless/5GTechSpec.htm
APPENDIX B
5G is the fifth generation of cellular technology. It is hard to tell from looking at a tower whether 5G is enabled or not. You would need a full electromagnetic frequency spectrum meter to know what the tower is transmitting and even then telecom companies can change the signal or argue that it is 4G. Suffice to say that all towers can be/will be 5G enabled if current plans proceed starting with those servicing high population areas. Demanding better cell phone service and buying smart devices encourages the rollout of 5G. It is the accumulation of such devices on top of all existing tech plus extended use into new frequencies that makes electromagnetic radiation from 5G such a problem.
APPENDIX C
“5G – Earth Under Attack”
“Australians for Safe Technology”
“5G – Toronto Under Attack”
